A/B Testing
Experiment Design + A/B Testing
A/B Testing
经典考法:
Phone Screening, 概念解释 eg. What is P Value
应用题 公司的应用场景描述问题,开放型,A/B Testing - 实验设计 - 假设检验
*证明题 Target PhD的
A/B Testing
A decision making procedure during product iteration. Experiment Design (collect customer log), Data Analysis and Hypothesis Testing.
Review可能会回到数据分析(engineering)或者重新A/B Testing。Ramp up:逐步上线,用户逐步从1到100%,launch:100%用户接触。
面试:最终的问题其实是,作为产品的负责人,怎么知道新的xx会不会比原来的xx更好? 在回答这种性质的面试问题时, 第一步:定义 什么是好 define the metrics to describe it. eg. revenue, CTR , the latter one reflects users' increase in their interests. 第二步:对比实验,比较前后的指标 第三步:实验设计,控制实验成本、风险,确定实验的有效性 第四步:假设检验,从实验数据中得到正确的结论
Metrics
**quantitative measurements that reflect the product quality.
面试:
好=赚钱, revenue+good user experience
从AARRR的沙漏模型上定义,可以是下图。
https://medium.com/@ms.mbalke/aarrr-framework-metrics-that-let-your-startup-sound-like-a-pirate-ship-e91d4082994b * 注意CTR是一个binary metric
Experiment and Randomized Experiments
Experiment: (not for internet company)
Randomized Experiment: counter factual, link 无法用上面的这样实验,因为在互联网公司,没办法让每个人看到广告后被洗脑、忘记过去的再看一个新的,即使是同一个人,今天心情好明天心情不好也会有一个随机性。
Pre-Post Design: (not for internet company) cognitive scores before and after neural operations
Enrollment: Eligible for the experiment, eg. if the target population is 'registered users' , etc. Take a representative sample from the full traffic, usually done by hashing the cookie id or random number generator (take 0.1 for example).
Randomized: select from the pool of people which group goes to experiment and which goes to the control group. The probability of being selected to any group is the same. It's independent of the users' characteristics and independent of the treatment. Done by coin flip or random number generator (take 0.5).
Novelty Effect: Version A and B in experiment should not differ too much, to avoid novelty effect. Aside from the difference itself, 新鲜感 wears off or 陌生感 brings bias to the metrics and thus influences the experiment.
(面试)Sampling Strategy/randomization strategy可能存在的问题:check for confounding factor的distribution是否balanced(也就是检查randomization 是否biased AA部分可以检验)。比如,1 sample continuous,划分地理位置的时候没有划分一致的大小,或者把Manhattan和Albany放在一起了,这就导致score的分母部分的方差偏大,score偏小,p value偏大,无法拒绝原假设。再或者,binary test,2 sample的 overall p离0.5近,那么standard error大,power减小,confidence interval变宽。
如何设计避免这种bias? 回答matching、segmentation。如果忘了matching,就用segmentation。
matching:sample the experiment group from the population, for each set of users in the experiment group, find a matched user from the rest of the population and put them in the control group. 可以one-to-one match on selected factors, set-to-set match on the frequency of the selected factors, one-to-one match on the frequency of the estimated propensity scores.
segmentation: divide the users into subsets and do analysis per segment. Can (1) help verify if there is heterogeneity in different subsets of users (male, female have different preference, etc.) (2) if confounding factors are imbalanced, segment-then-unify can be an alternative to matching.
和AB Testing有关的名词解释 链接
以下是 如何根据AB Testing所定义的metric的不同,利用HT得出结论。
Hypothesis Testing
Intuition: Why HT?
Due to the randomness in the data, the estimate of the parameters is also random. HT is the procedure to determine if the estimated difference is a statistically meaningful difference.
Key Concepts
Null Hypothesis H0: A specific claim about the population, often described using an expression of the parameter(s).
Alternative Hypothesis Hα : The claim about the population when the null hypothesis is false (parameter of interest: =,><0 ).
P-value: The probability of obtaining as or more extreme results than the current observation, under the null hypothesis.
Significance Level α : Type 1 Error Rate, the probability of rejecting H0 given H0 is true. P(rejH0∣H0is true)
H0 是想要推翻的假设, Hα是想要证明的假设。绝大多数的A/B Testing中的HT:
H0 是 δmetric=0 , Hα可以是双尾(=),单尾(> 或<0)。
"Is A better than B? " Hα:metricA−metricB>0
"Can you tell me if there is a difference?" Hα:metricA−metricB=0
"Which one is better?" "Let's assume we can run a two-tail hypothesis testing"
Type 1 Error: This happens when H0 is true, but is rejected. 无中生有
Significance Level = Type 1 Error Rate = P(rejH0∣H0is true)
Confidence Level = 1-significance level
Type 2 Error: This happens when Hα is true, but H0 is not rejected. 有眼无珠
Type 2 Error Rate: β=Pr( not rej H0∣H1 is true )=1−Pr( rej H0∣H1 is true)
Power: The probability of rejecting H0 , when Hα is true. power=Pr(rejH0∣H1 is true) =1−β
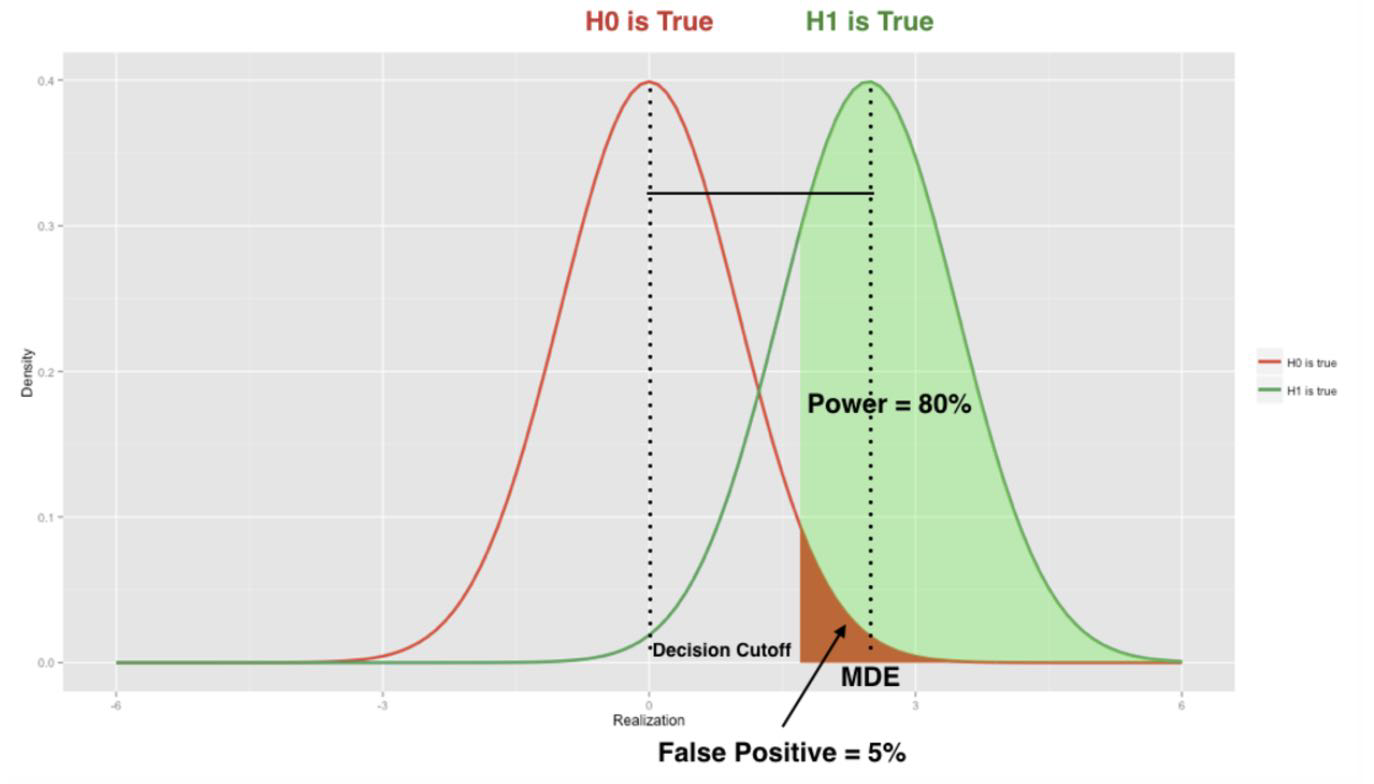
Why Significance Level = Type 1 Error Rate ?
P-value is a random variable because it's a function of a random variable. {p -value ∣H0 is true} − Uniform (0,1),Pr( uniform variable <x)=x, for x in (0,1)
Type 1 error rate =Pr( reject H0∣H0 is true) =Pr( p-value < significance level ∣H0 is true) = significance level
Trade off between type 1 and type 2 error
可以默认Type1 Error (convicting an innocent man) 比Type 2 Error (releasing a criminal)更严重,所以在实际操作中,优先降低Type1 Error,其次尽可能降低Type 2 Error。为此,设置一个比较小的 α=0.05 , 然后尽可能收集更多的数据,来获得更多的power β (或者也可以设计其他的 less variable metric)。
eg. If we want to analyze the H0: students at xx have an average height of 7 feet (2.13m).
Let's say H0:μ=7feet , then Hα:μ=7feet . We first assume the null hypothesis to be true. Then take a random sampling from the population (the sample represents well the population), know of the average height of the sample is X=5′9′′ . If the null is true, then if we enter any random classroom and draw the histogram of this parameter, the histogram (hypothetically) will look like a mean of 7 and a bell-shape distribution. Also, in that histogram, X=5′9′′ will fall to the left end.
So the key-point in here is 'if the null hypothesis is true, what's the histogram gonna look like'
social-network中,不能单纯用P value,因为nodes之间不再是independent。所以原来的“如果p<0.05, reject the null hypothesis H0“就不对了。
Hypothesis Testing as an Algorithm
前提条件:
A/B Testing (randomized experiment)中的假设检验
Metric以均值的形式定义 - CTR,DAU(daily active user), ARPU(annual revenue per user) 与之相对的是,类似ROI这样的metric,这就不是简单的均值,就不适用于以下方法 所以在面试中,尽力把metric定义成均值的形式 也尽量让feature 是 binary data的均值或者continuous feature的均值
θ^n Metric的估计值
θ∗ 零假设成立时的metric的真实值
SD(θ^n) 零假设成立时的方差,等于根号下sample的方差/sample size
1)"抛硬币100次,60次head,这个硬币是否biased", 是一个One Sample Test。
p^=0.6 数据算出来的均值, p0=0.5 原假设下的均值, z=(0.6-0.5)/sqrt(0.5*0.5)/100)=2
另外,医疗行业还有paired design 每个观测数据点都测了两次metric,治病前vs后,但是最后其实我们关注的是这两次metric的difference。这种只做one group test是因为被测对象前后是同一批人,组内数据是有关系的,不能做two group test。
2)A/B Testing背景下的HT多是Two Sample Test, p1和p2分别是A和B group。比如A 200/1000, B 300/1000
p^1=1000200 是A组的平均值, p^2=1000300 是B组的平均值, p^=1000500 是两组数据合在一起的overall均值.
Cumulative Distribution Function F(x)=P(x<=x)
P-value Fnormal(−∣Z∣)
3)连续变量,2 sample的test score的公式都一样;但如果假设了数据是正态分布,那么最后test score服从t distribution;
而不假设正态分布,得到的test score可以近似认为是0~1 Normal。 注意在平时不要随便假设数据正态分布,因为太少见了。医学实验、clinical trial,无奈之下才会强行假设test的指标服从Gaussian分布。这时的df有一个近似公式,在两组方差比较接近、sample size也接近时,df=sample size-2
事实上,数据越大(>30 per group),越不需要对数据的分布做假设,因为中央极限定理,平均值本身就服从了正态分布。
standard error = estimator的SD
p-value 假设数据遵从Gaussian: Ft(−∣S∣)df
p-value 不假设数据遵从Gaussian: Fnormal(−∣Z∣)
假如双尾,上面的p-value*2
如果 p-value <=alpha, 就reject H0;否则,‘you don't have sufficient evidence to reject H0。 Cannot make conclusive result’ , 但是不代表H1就正确!!!
Hypothesis Testing Algorithm Explained
BG Knowledge 1: Central Limit Theorem
Formal Definition
随机变量序列 {X1,X2,…} ,i.i.d., E[Xi]=μ , Var[Xi]=σ2<∞ . 随着n趋向无穷, n(X−μ) 收敛于(is convergence in distribution to) N(0,σ2)
Note: Cuchy distribution, variance = infinity , so it does not follow CLT
Notation D: converge to distribution
如果上式左右同时除以sigma,那么我们就得到了上一小节Non-Gaussian里的One Sample or Paired的情况, Z=σ^2/nX−μ0→DN(0,1) 。这也就证明了为什么N-->infinity时均值服从正态分布。
Difference between CLT and 大数定理
大数定理是括号里的部分converge in probability,如果想要让它收敛速度变慢,就乘以 n
Casual Definition
无偏估计,sample mean的均值 E(X)=E(n1∑i=1nXi)=n1∑i=1nE(Xi)=n1×nE(Xi)=μ
等于population的均值。假设我们的参数 θ 本身就是均值,那么E[θ^n(X)]=θ∗ ,右边的*是population true value,对真实数据的估计值是 θ^n(X) 。
当n足够大时, SD(θ^n)θ^n−θ∗→DN(0,1)
SD(θ^n) 是零假设成立时对标准差的估计值。By Slutsky's theorem, SD(θ^n) 可以是population的true standard deviation, 也同样可以是sample的standard deviation.
BG Knowledge 2: Distribution
Normal Distribution 均值和方差确定,distribution就确定了
Chi-squared Distribution k个独立标准正态分布随机变量的平方和就是自由度为k的chi-square distribution 由df决定形状
T distribution df决定形状 df=1时是heavy tail、fat tail,当df=infinity时,t distribution就是标准正态分布 所以可以理解为 standard normal distribution是t distribution的特例。
T=X/kZ, where Z∼N(0,1),X∼χ2(k),Z and X are independent. k is df
Binomial Distribution Mean:np, SD: np(1-p)
Multinomial Distribution
Poisson distribution
Equations, prove (interview, PhD)
t=σ^2/nX−μ0∼tdf=n−1 把分母的 n 乘上去,无偏估计, Xˉ = μ^ , 上下同时除以 σ(假设population存在一个sigma) , 再在分母上做一些变换,得到 [(n−1)σ^2/σ2]/(n−1)n(μ^−μ0)/σ 。分子部分就遵循了exact definition的CLT, N(0,1) 。 分母部分,因为data本身是independent normally distributed random variables, with mean μ , SD σ . By Cochran's Theorem,这是一个自由度为n-1的chi-square distribution。 所以这两个的ratio就满足了T-distribution的定义。
Z=σ^2/nX−μ0→DN(0,1) 如果数据本身不遵循normal distribution,但n很大(n>30),Xˉ=μ^=θ^n(X) , μ0=θ∗ ,那么 SD(μ^)=Var(X)=n21∑i=1nVar(X)=nσ2 ,其中的 σ 可以替换成 σ^ , 遵循了casual definition的CLT, N(0,1).
Sample Size Calculation
连续变量: (Zα/2+Zβ)2∗2∗σ2/d2
binary变量: (Zα/2+Zβ)2∗(p1(1−p1)+p2(1−p2))/(p1−p2)2
其中 Zα/2 是significance level是alpha的双尾测试时的critical value(也就是z score)
注意
不要假设data是normal distribution,另外normality test不能证明,只能证伪。因为normality test的 H0 是“ is Normal”, H1 是“is not Normal”。
补充
如果Binary Data,数据样本太小,用Fisher Exact Test; 如果Binary Data, p过大或过小,用Permutation Test
如果Continuous Data,样本太小,Bootstrap Test,如果样本够大但是heavy tail(long tail,比如收入),也用Bootstrap Test。HT cover到0,显著;不能cover到0,不显著
如果把数据分成了m组,每组都设定了alpha的significance level,比如按照地理划分,使用同样的H0,那到最后也不知道总体的Type 1 error rate. By Bonferroni correction, 就可以在family wise error rate做一个control。但是它过于conservative,比如如果有1000个group,那么每一个alpha就过小。这时FDR是一个更好的approach。
False Discovery Rate (FDR)adjustment可以让Type 1 error rate控制在某一个比例之中,对individual p value做correction。
ANOVA的一个应用:likelihood ratio test
H0 在AB Testing都是=0,如果是一个范围,用composite test
Python或R中一行得到cdf或者p value的代码:
from scipy.stats import normnorm.cdf(value) pnorm(value)
About Sampling
Simple Random Sampling
Systematic Sampling
Sampling with probability proportional to size
Stratified sampling
Cluster Sampling
Multi-stage sampling
Multi-phase sampling
Last updated

